Open-die Drop Forging
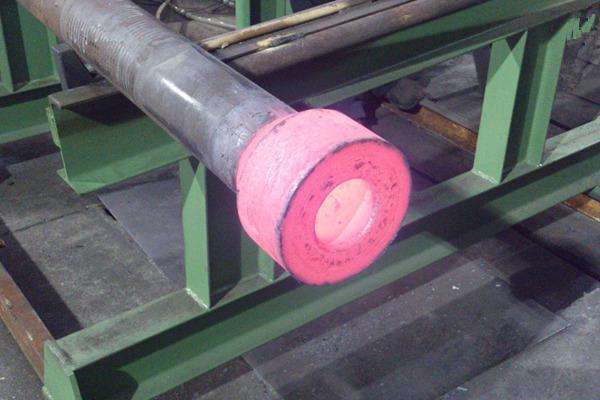
In open-die forging, a hammer strikes and deforms the workpiece, which is placed on a stationary anvil. Open-die forging gets its name from the fact that the dies (the surfaces that are in contact with the workpiece) do not enclose the workpiece, allowing it to flow except where contacted by the dies. The operator therefore needs to orient and position the workpiece to get the desired shape. The dies are usually flat in shape, but some have a specially shaped surface for specialized operations. For example, a die may have a round, concave, or convex surface or be a tool to form holes or be a cut-off tool. Open-die forgings can be worked into shapes which include discs, hubs, blocks, shafts (including step shafts or with flanges), sleeves, cylinders, flats, hexes, rounds, plate, and some custom shapes. Open-die forging lends itself to short runs and is appropriate for art smithing and custom work. In some cases, open-die forging may be employed to rough-shape ingots to prepare them for subsequent operations. Open-die forging may also orient the grain to increase strength in the required direction.
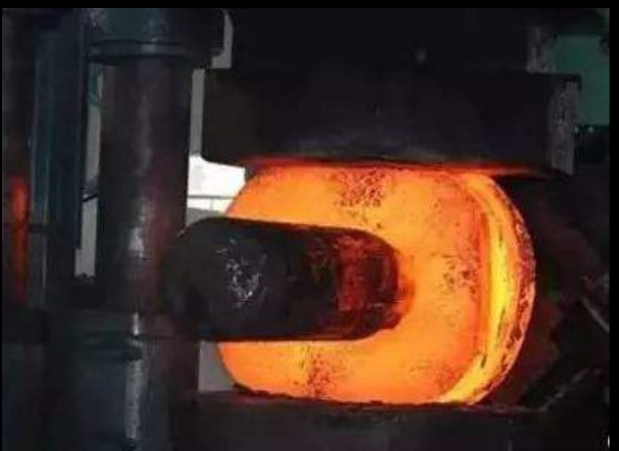

Impression-die Forging
In impression-die forging, the metal is placed in a die resembling a mold, which is attached to an anvil. Usually, the hammer die is shaped as well. The hammer is then dropped on the workpiece, causing the metal to flow and fill the die cavities. The hammer is generally in contact with the workpiece on the scale of milliseconds. Depending on the size and complexity of the part, the hammer may be dropped multiple times in quick succession. Excess metal is squeezed out of the die cavities, forming what is referred to as "flash". The flash cools more rapidly than the rest of the material; this cool metal is stronger than the metal in the die, so it helps prevent more flash from forming. This also forces the metal to completely fill the die cavity. After forging, the flash is removed.
Upset Forging
Upset forging increases the diameter of the workpiece by compressing its length. Based on number of pieces produced, this is the most widely used forging process. A few examples of common parts produced using the upset forging process are engine valves, couplings, bolts, screws, and other fasteners.